Science Behind OrCam
At OrCam, a commitment to scientific excellence is at the heart of everything we do.
Our dedication to cutting-edge research and scientific advancement drives us to push the boundaries of assistive technology.
By harnessing the potential of artificial intelligence and groundbreaking algorithms, we transform scientific principles into reality, bridging the gap between science and real-world impact to help individuals who are visually impaired and have learning challenges regain confidence, and a renewed freedom with our AI solutions.
Our Reviewers
OrCam MyEye
OrCam MyEye, our flagship solution represents a pioneering assistive device that has revolutionized the perceptual experience for individuals with visual impairments.
This wearable device harnesses state-of-the-art artificial intelligence and computer vision algorithms to empower individuals with visual impairments, fostering a remarkable sense of independence, freedom, and confidence.
OrCam Read
The OrCam Read stands as an innovative assistive device with remarkable capabilities, positioned to revolutionize the reading experience for individuals with low vision and visual impairments including reading difficulties related to age-related vision loss, mild to moderate low vision or reading fatigue.
Driven by advanced technology and grounded in scientific research, the OrCam Read marks a transformative breakthrough in making printed and digital text accessible with precise laser guidance.
OrCam Learn
OrCam Learn is an inventive educational tool engineered to empower individuals across diverse age groups and abilities. Supported by a foundation of scientific research and rigorous studies, OrCam Learn harnesses cutting-edge technology to enhance accessibility and engagement in the learning process.
Whether one is a student, educator, or lifelong learner, this formidable device proves instrumental in fostering reading comprehension, expanding vocabulary, and facilitating the acquisition of foreign languages. With its intuitive interface and tailored approach, OrCam Learn dynamically adapts to individual learning styles, delivering real-time feedback and personalized guidance.

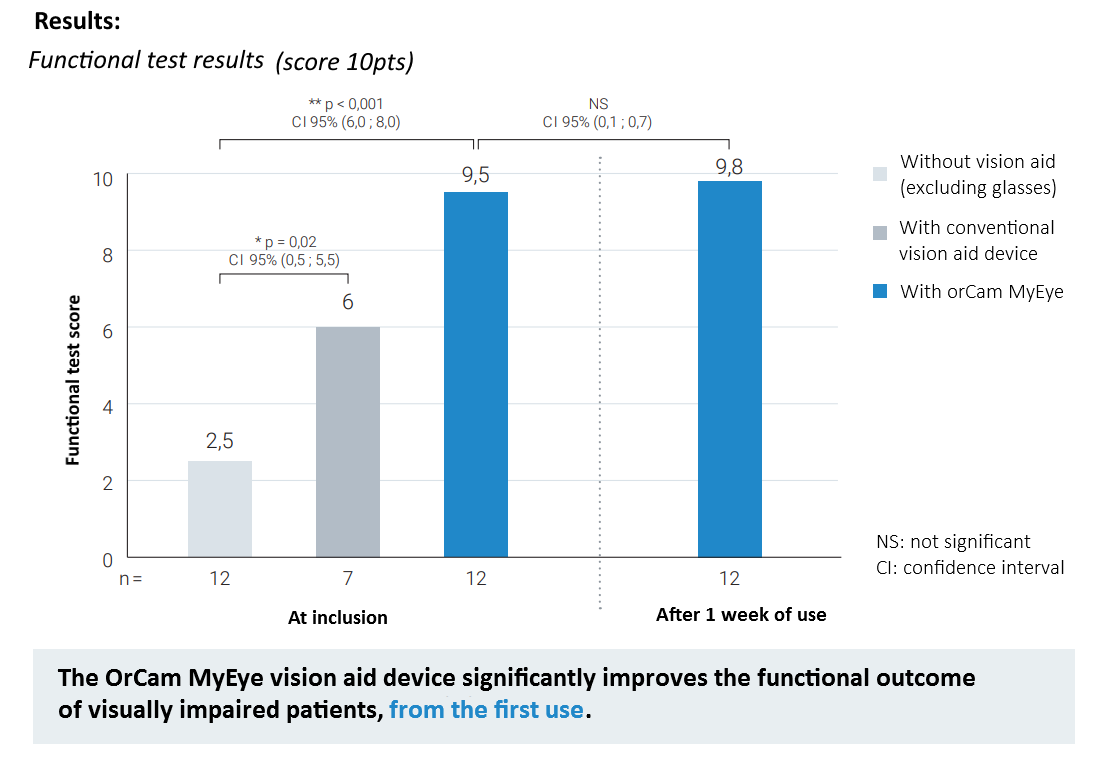
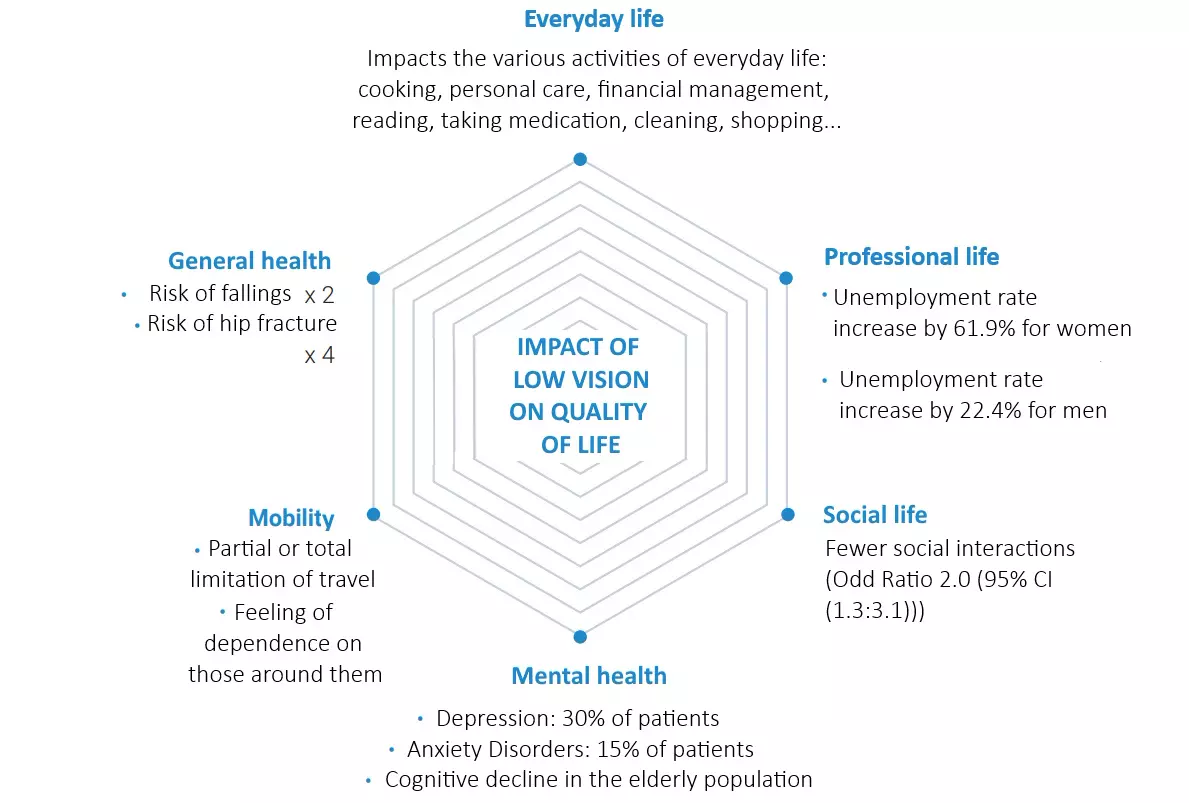
OrCam MyEye Studies
OrCam Read Studies
Reasearch With Us
Interested in learning more about OrCam's researches and technology?
Fill out the form, and we'll get back to you shortly.










